Querying Internal Tables
1. Preparation Work
There is no difference in the query interface between internal table queries and model queries. For details, refer to SQL Queries.
You do not need to rewrite any SQL, but you must ensure that all tables you are querying have had internal tables created and have imported data.
2. Querying Internal Tables
In the Kylin query interface, you can check the "Query Internal Table" option to skip the model matching phase. If you are certain that your query is a flexible query that cannot be answered through the pre-calculated indexes of the model, checking "Direct Query Internal Table" can save model matching time and thus improve query response speed.
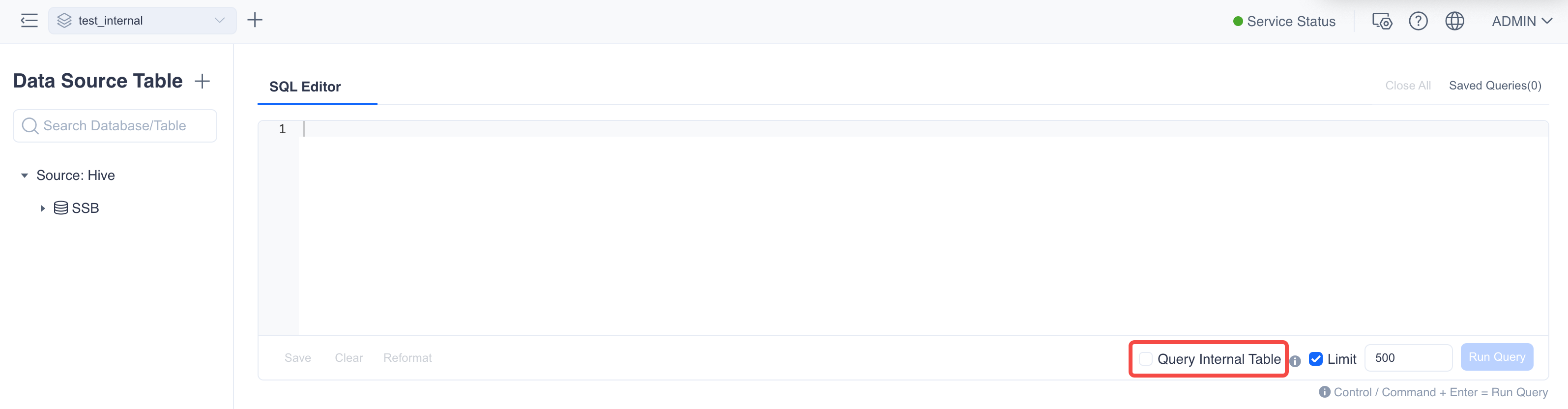
By default, "Query Internal Table" is not checked. At this time, the query engine will first prioritize model matching with pre-calculated indexes. When it cannot be answered through the pre-calculated indexes, it will switch to direct querying of the internal table. If part of a complex query can be answered through the model index and part cannot, the system will attempt to answer through a combination of model indexes and internal table joins.
3. Push Down Queries
After the internal table feature is enabled, regardless of whether the tables in the query have been created as internal tables or whether data has been imported, the query will no longer be pushed down to the data source.