Kylin on Cloud — Build A Data Analysis Platform on the Cloud in Two Hours Part 1
Video Tutorials
Kylin on Cloud — Build A Data Analysis Platform on the Cloud in Two Hours Part 1
Background
Apache Kylin is a multidimensional database based on pre-computation and multidimensional models. It also supports standard SQL query interface. In Kylin, users can define table relationships by creating Models, define dimensions and measures by creating Cubes, and run data aggregation with Cube building. The pre-computed data will be saved to answer user queries and users also can perform further aggregation on the pre-computed data, significantly improving the query performance.
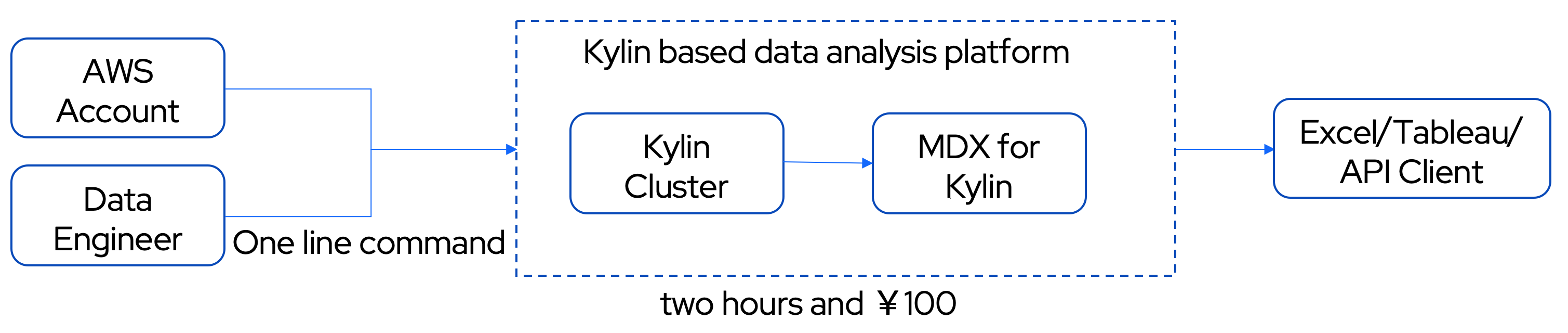
With the release of Kylin 4.0, Kylin can now be deployed without a Hadoop environment. To make it easier for users to deploy Kylin on the cloud, Kylin community recently developed a cloud deployment tool that allows users to obtain a complete Kylin cluster by executing just one line of command, delivering a fast and efficient analysis experience for the users. Moreover, in January 2022, the Kylin community released MDX for Kylin to enhance the semantic capability of Kylin as a multidimensional database. MDX for Kylin provides the MDX query interface, users can define business metrics based on the multidimensional model and translate the Kylin data models into a business-friendly language to give data business values, making it easier to integrate with Excel, Tableau, and other BI tools.
With all these innovations, users can easily and quickly deploy Kylin clusters on the cloud, create multi-dimensional models, and enjoy the short query latency brought by pre-computation; what’s more, users can also use MDX for Kylin to define and manage business metrics, leveraging both the advantages of data warehouse and business semantics.
With Kylin + MDX for Kylin, users can directly work with BI tools for multidimensional data analysis, or use it as the basis to build complex applications such as metrics platforms. Compared with the solution of building a metrics platform directly with computing engines such as Spark and Hive that perform Join and aggregated query computation at runtime, Kylin, with our multidimensional modeling, pre-computation technology, and semantics layer capabilities empowered by MDX for Kylin, provides users with key functions such as massive data computation, extremely fast query response, unified multidimensional model, interface to a variety of BI tools, and basic business metrics management capabilities.
This tutorial will start from a data engineer’s perspective to show how to build a Kylin on Cloud data analysis platform, which will deliver a high-performance query experience for hundreds of millions of rows of data with a lower TCO, the capability to manage business metrics through MDX for Kylin, and direct connection to BI tools for quick reports generating.
Each step of this tutorial is explained in detail with illustrations and checkpoints to help newcomers. All you need to start is to an AWS account and 2 hours. Note: The cloud cost to finish this tutorial is around 15$.
Business scenario
Since the beginning of 2020, COVID-19 has spread rapidly all over the world, which has greatly changed people’s daily life, especially their travel habits. This tutorial wants to learn the impact of the pandemic on the New York taxi industry based on the pandemic data and New York taxi travel data since 2018 and indicators such as positive cases, fatality rate, taxi orders, and average travel mileage will be analyzed. We hope this analysis could provide some insights for future decision-making.
Business issues
- The severity of the pandemic in different countries and regions
- Travel metrics of different blocks in New York City, such as order number, travel mileage, etc.
- Does the pandemic have a significant impact on taxi orders?
- Travel habits change after the pandemic (long-distance vs. short-distance travels)
- Is the severity of the pandemic strongly related to taxi travel?
Dataset
COVID-19 Dataset
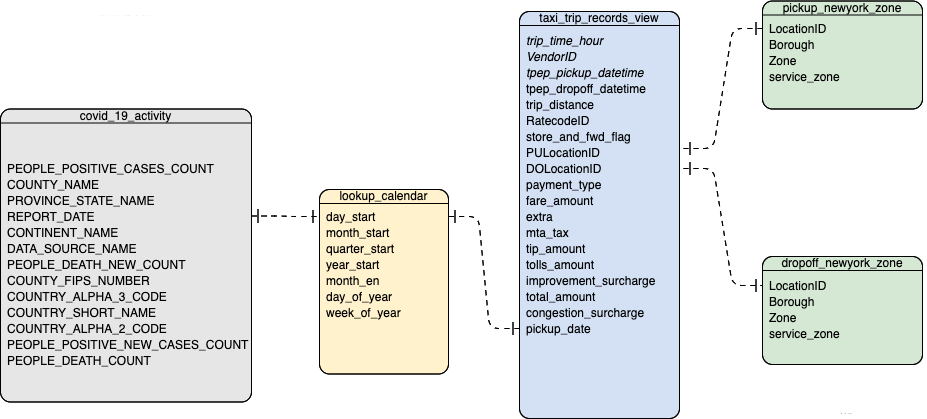
The COVID-19 dataset includes a fact table covid_19_activity and a dimension table lookup_calendar.
covid_19_activity contains the number of confirmed cases and deaths reported each day in different regions around the world. lookup_calendar is a date dimension table that holds time-extended information, such as the beginning of the year, and the beginning of the month for each date. covid_19_activity and lookup_calendar are associated by date.
COVID-19 数据集相关信息如下:
| Data size | 235 MB |
| Fact table row count | 2,753,688 |
| Data range | 2020-01-21~2022-03-07 |
| Download address provided by the dataset provider | https://data.world/covid-19-data-resource-hub/covid-19-case-counts/workspace/file?filename=COVID-19+Activity.csv |
| S3 directory of the dataset | s3://public.kyligence.io/kylin/kylin_demo/data/covid19_data/ |
NYC taxi order dataset
The NYC taxi order dataset consists of a fact table taxi_trip_records_view, and two dimension tables, newyork_zone and lookup_calendar.
Among them, each record in taxi_trip_records_view corresponds to one taxi trip and contains information like the pick-up ID, drop-off ID, trip duration, order amount, travel mileage, etc. newyork_zone records the administrative district corresponding to the location ID. taxi_trip_records_view are connected with newyork_zone through columns PULocationID and DOLocationID to get the information about pick-up and drop-off blocks. lookup_calendar is the same dimension table as in the COVID-19 dataset. taxi_trip_records_view and lookup_calendar are connected by date.
NYC taxi order dataset information:
| Data size | 19 G |
| Fact table row count | 226,849,274 |
| Data range | 2018-01-01~2021-07-31 |
| Download address provided by the dataset provider | https://www1.nyc.gov/site/tlc/about/tlc-trip-record-data.page |
| S3 directory of the dataset | s3://public.kyligence.io/kylin/kylin_demo/data/trip_data_2018-2021/ |
ER Diagram
The ER diagram of the COVID-19 dataset and NYC taxi order dataset is as follows:
Metrics design
Based on what we try to solve with this model, we designed the following atomic metrics and business metrics:
1. Atomic metrics
Atomic metrics refer to measures created in Kylin Cube, which are relatively simple, as they only run aggregated calculations on one column.
- Covid19 case count:
sum(covid_19_activity.people_positive_cases_count) - Covid19 fatality:
sum(covid_19_activity. people_death_count) - Covid19 new positive case count:
sum(covid_19_activity. people_positive_new_cases_count) - Covid19 new death count:
sum(covid_19_activity. people_death_new_count) - Taxi trip mileage:
sum(taxi_trip_records_view. trip_distance) - Taxi order amount:
sum(taxi_trip_records_view. total_amount) - Taxi trip count:
count() - Taxi trip duration:
sum(taxi_trip_records_view.trip_time_hour)
2. Business metrics
Business metrics are various compound operations based on atomic metrics that have specific business meanings.
- MTD, YTD of each atomic metric
- MOM, YOY of each atomic metric
- Covid19 fatality rate: death count/positive case count
- Average taxi trip speed: taxi trip distance/taxi trip duration
- Average taxi trip mileage: taxi trip distance/taxi trip count
Operation Overview
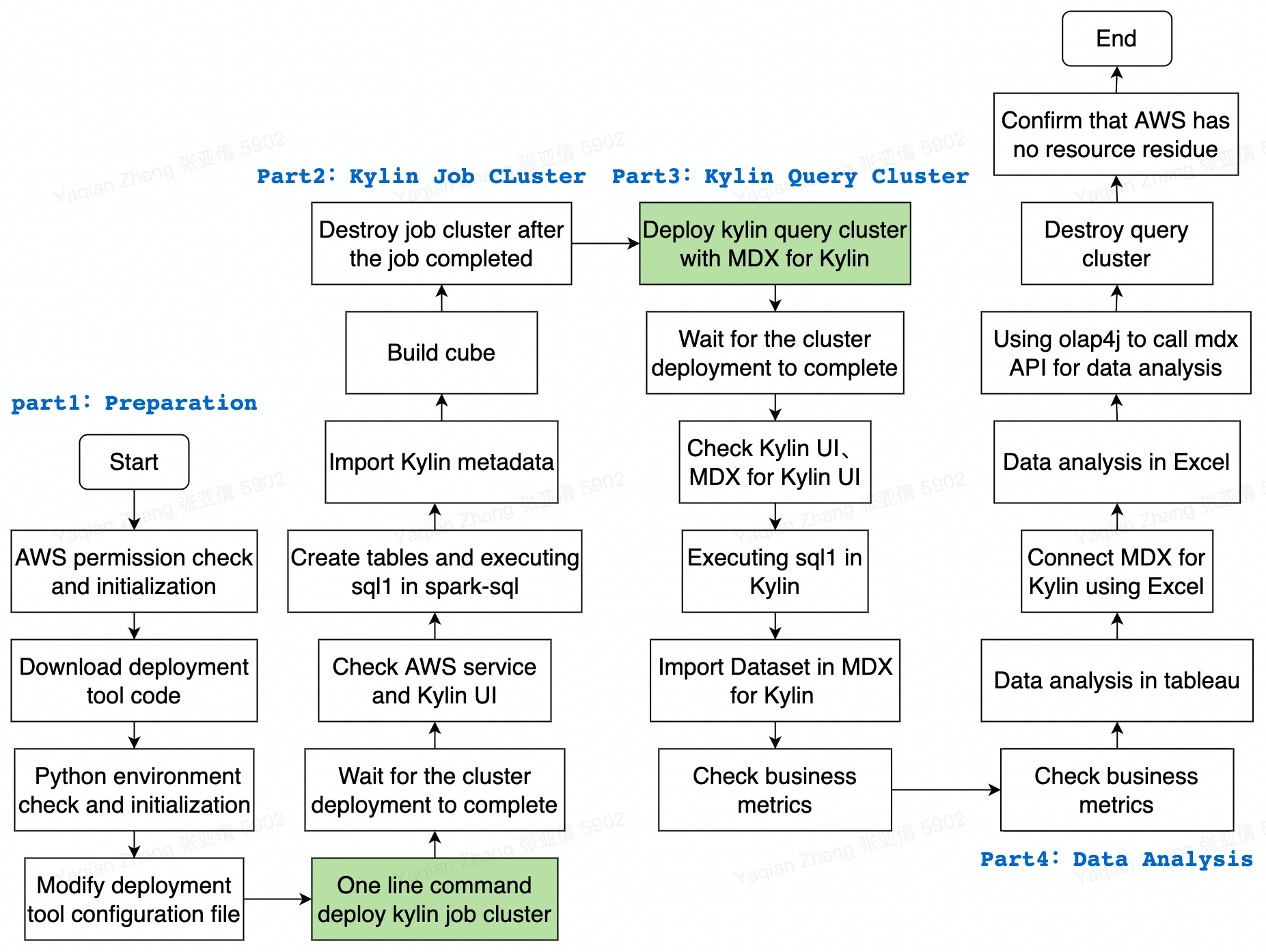
The diagram below is the main steps to build a cloud data analysis platform with Apache Kylin and how to perform data analysis:
Cluster architecture
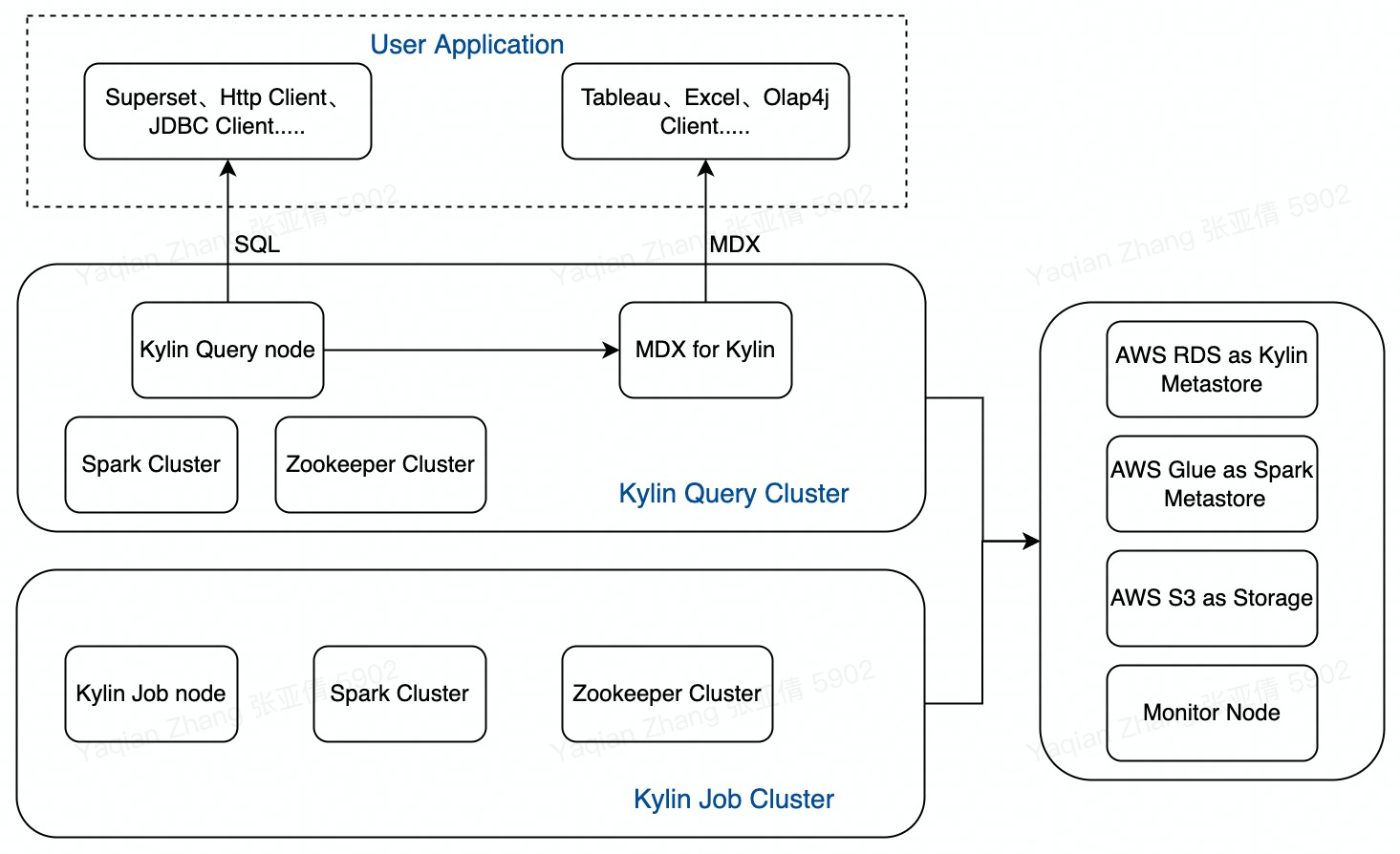
Here is the architecture of the Kylin cluster deployed by the cloud deployment tool:
Kylin on Cloud deployment
Prerequisites
- GitHub Desktop: for downloading the deployment tool;
- Python 3.6.6: for running the deployment tool
AWS permission check and initialization
Log in to AWS with your account to check the permission status and then create the Access Key, IAM Role, Key Pair, and S3 working directory according to the document Prerequisites. Subsequent AWS operations will be performed with this account.
Configure the deployment tool
-
Execute the following command to clone the code for the Kylin on AWS deployment tool.
shell git clone -b kylin4_on_cloud --single-branch https://github.com/apache/kylin.git && cd kylin -
Initialize the virtual environment for your Python on local machine.
Run the command below to check the Python version. Note: Python 3.6.6 or above is needed:
shell python --versionInitialize the virtual environment for Python and install dependencies:
shell bin/init.sh source venv/bin/activate -
Modify the configuration file
kylin_configs.yaml
Open kylin_configs.yaml file, and replace the configuration items with the actual values:
AWS_REGION: Region for EC2 instance, the default value iscn-northwest-1${IAM_ROLE_NAME}: IAM Role just created, e.g.kylin_deploy_role${S3_URI}: S3 working directory for deploying Kylin, e.g. s3://kylindemo/kylin_demo_dir/${KEY_PAIR}: Key pairs just created, e.g. kylin_deploy_key${Cidr Ip}: IP address range that is allowed to access EC2 instances, e.g. 10.1.0.0/32, usually set as your external IP address to ensure that only you can access these EC2 instances
As Kylin adopts a read-write separation architecture to separate build and query resources, in the following steps, we will first start a build cluster to connect to Glue to create tables, load data sources, and submit build jobs for pre-computation, then delete the build cluster but save the metadata. Then we will start a query cluster with MDX for Kylin to create business metrics, connect to BI tools for queries, and perform data analysis. Kylin on AWS cluster uses RDS to store metadata and S3 to store the built data. It also supports loading data sources from AWS Glue. Except for the EC2 nodes, the other resources used are permanent and will not disappear with the deletion of nodes. Therefore, when there is no query or build job, users can delete the build or query clusters and only keep the metadata and S3 working directory.
Kylin build cluster
Start Kylin build cluster
-
Start the build cluster with the following command. The whole process may take 15-30 minutes depending on your network conditions.
shell python deploy.py --type deploy --mode job -
You may check the terminal to see if the build cluster is successfully deployed:
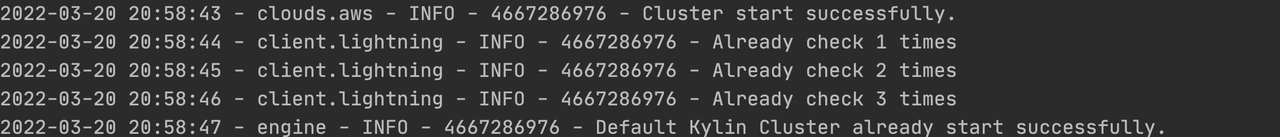
Check AWS Service
-
Go to CloudFormation on AWS console, where you can see 7 stacks are created by the Kylin deployment tool:
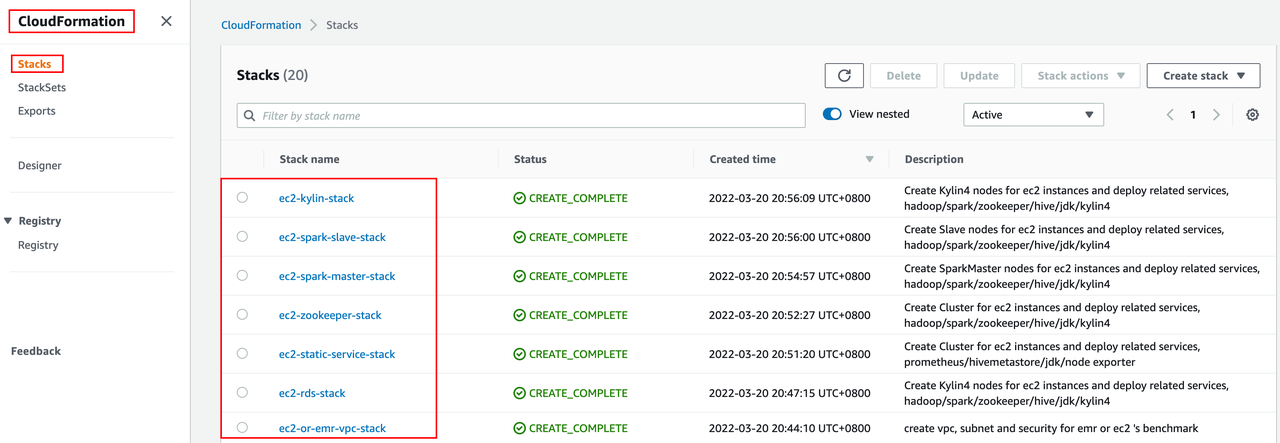
-
Users can view the details of EC2 nodes through the AWS console or use the command below to check the names, private IPs, and public IPs of all EC2 nodes.
python deploy.py --type list
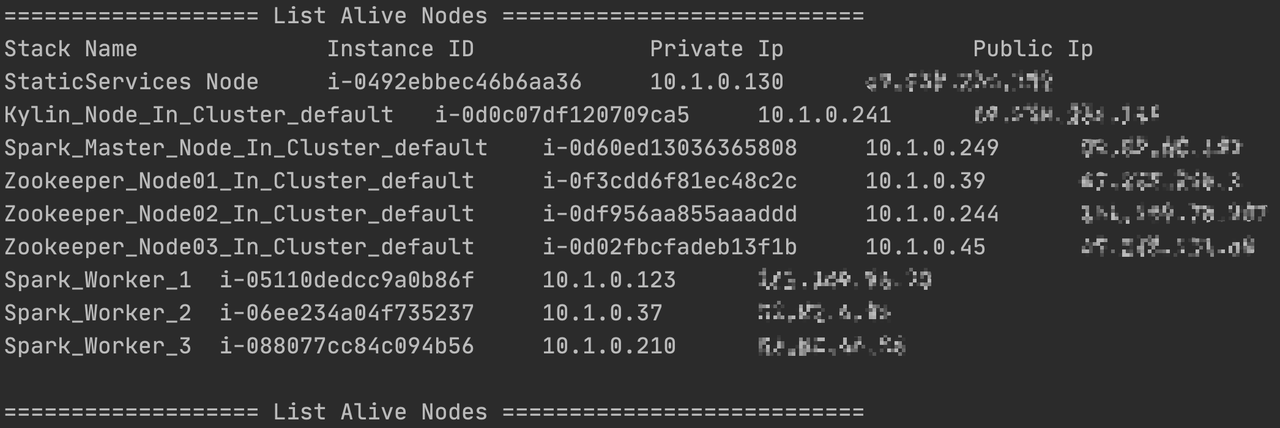
Spark-SQL query response time
Let’s first check the query response time in Spark-SQL environment as a comparison.
-
First, log in to the EC2 where Kylin is deployed with the public IP of the Kylin node, switch to root user, and execute
~/.bash_profileto implement the environment variables set beforehand.shell ssh -i "${KEY_PAIR}" ec2-user@${kylin_node_public_ip} sudo su source ~/.bash_profile -
Go to
$SPARK_HOMEto modify configuration fileconf/spark-defaults.conf, change spark_master_node_private_ip to a private IP of the Spark master node:```shell
cd $SPARK_HOME
vim conf/spark-defaults.conf## Replace spark_master_node_private_ip with the private IP of the real Spark master node
spark.master spark://spark_master_node_private_ip:7077
```In
spark-defaults.conf, the resource allocation for driver and executor is the same as that for Kylin query cluster. -
Create table in Spark-SQL
All data from the test dataset is stored in S3 bucket of
cn-north-1andus-east-1. If your S3 bucket is incn-north-1orus-east-1, you can directly run SQL to create the table; Or, you will need to execute the following script to copy the data to the S3 working directory set up inkylin_configs.yaml, and modify your SQL for creating the table:```shell
## AWS CN user
aws s3 sync s3://public.kyligence.io/kylin/kylin_demo/data/ ${S3_DATA_DIR} –region cn-north-1## AWS Global user
aws s3 sync s3://public.kyligence.io/kylin/kylin_demo/data/ ${S3_DATA_DIR} –region us-east-1## Modify create table SQL
sed -i “s#s3://public.kyligence.io/kylin/kylin_demo/data/#${S3_DATA_DIR}#g” /home/ec2-user/kylin_demo/create_kylin_demo_table.sql
```Execute SQL for creating table:
shell bin/spark-sql -f /home/ec2-user/kylin_demo/create_kylin_demo_table.sql -
Execute query in Spark-SQL
Go to Spark-SQL:
shell bin/spark-sqlRun query in Spark-SQL:
sql use kylin_demo; select TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW.PICKUP_DATE, NEWYORK_ZONE.BOROUGH, count(*), sum(TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW.TRIP_TIME_HOUR), sum(TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW.TOTAL_AMOUNT) from TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW left join NEWYORK_ZONE on TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW.PULOCATIONID = NEWYORK_ZONE.LOCATIONID group by TAXI_TRIP_RECORDS_VIEW.PICKUP_DATE, NEWYORK_ZONE.BOROUGH;We can see that with the same configuration as Kylin query cluster, direct query using Spark-SQL takes over 100s:

-
After the query is successfully executed, we should exit the Spark-SQL before proceeding to the following steps to save resources.
Import Kylin metadata
-
Go to
$KYLIN_HOMEshell cd $KYLIN_HOME -
Import metadata
shell bin/metastore.sh restore /home/ec2-user/meta_backups/ -
Reload metadata
Type http://${kylin_node_public_ip}:7070/kylin (relace the IP with the public IP of the EC2 node) in your browser to log in to Kylin web UI, and log in with the default username and password ADMIN/KYLIN:
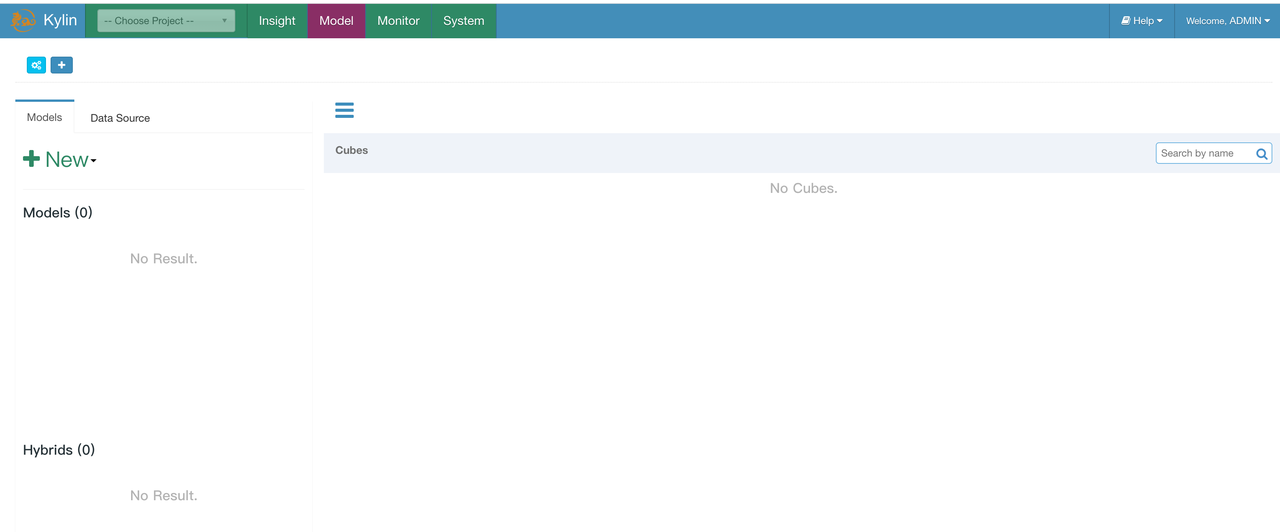
Reload Kylin metadata by clicking System - > Configuration - > Reload Metadata:
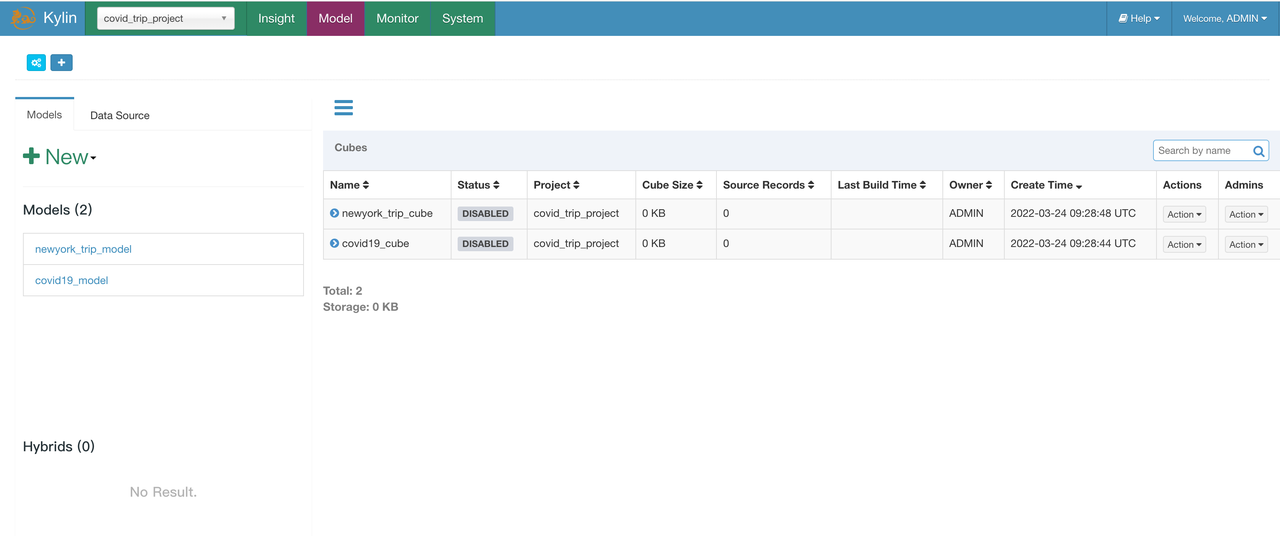
If you’d like to learn how to manually create the Model and Cube included in Kylin metadata, please refer to Create model and cube in Kylin.
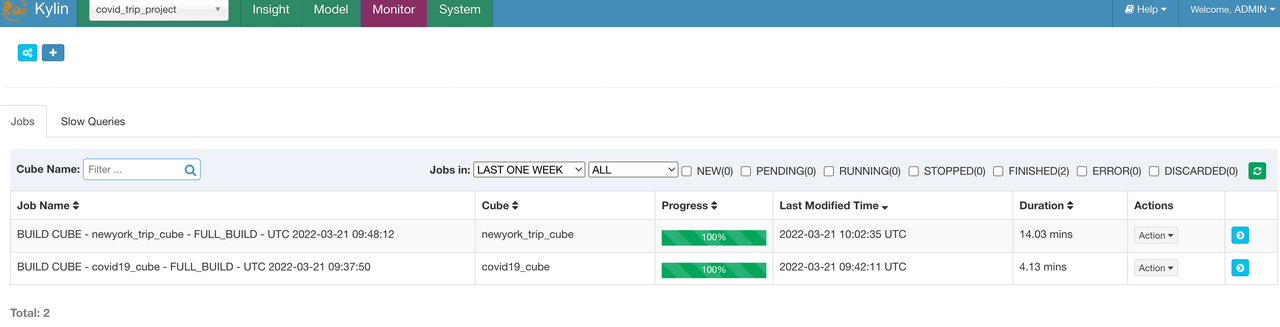
Run build
Submit the Cube build job. Since no partition column is set in the model, we will directly perform a full build for the two cubes:

Destroy build cluster
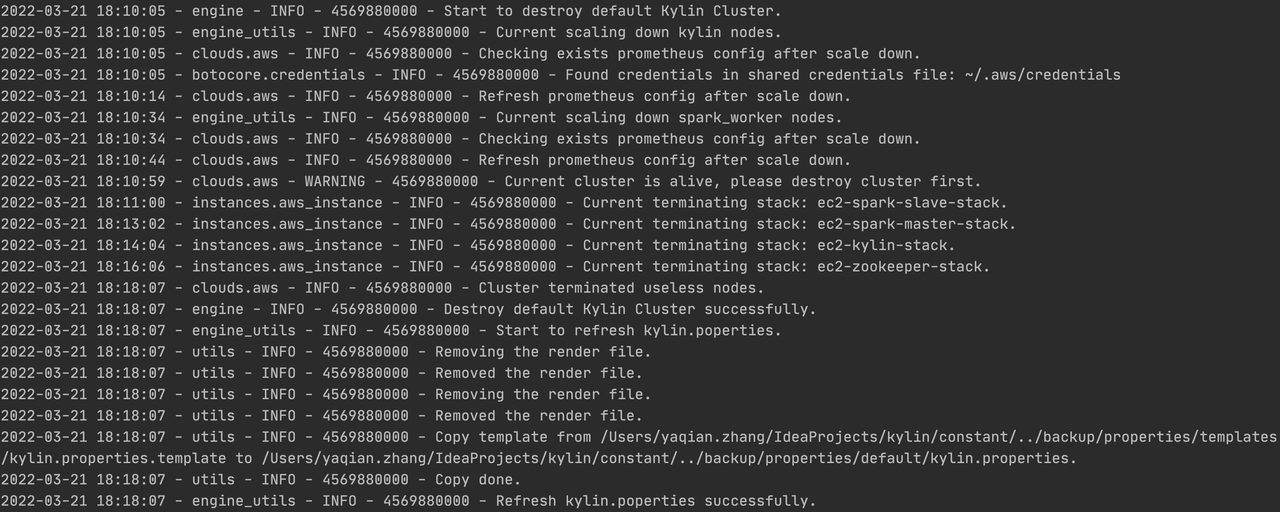
After the building Job is completed, execute the cluster delete command to close the build cluster. By default, the RDS stack, monitor stack, and VPC stack will be kept.
python deploy.py --type destroy
Cluster is successfully closed:
Check AWS resource
After the cluster is successfully deleted, you can go to the CloudFormation page in AWS console to confirm whether there are remaining resources. Since the metadata RDS, monitor nodes, and VPC nodes are kept by default, you will see only the following three stacks on the page.
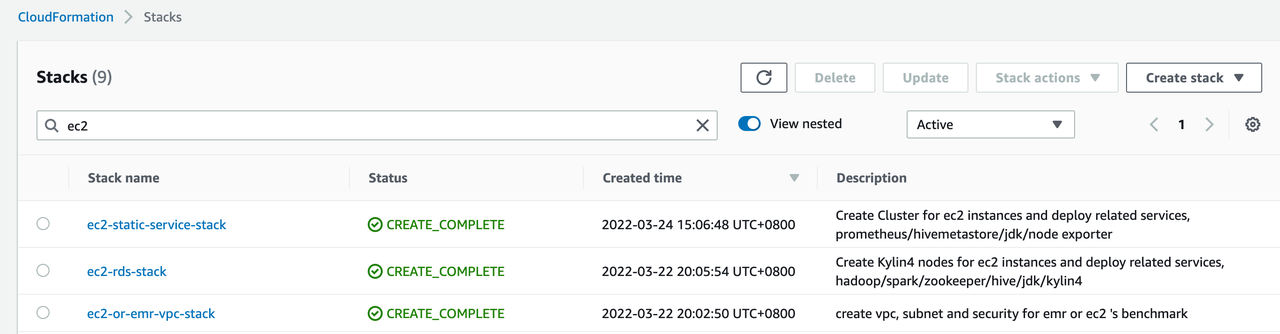
The resources in the three stacks will still be used when we start the query cluster, to ensure that the query cluster and the build cluster use the same set of metadata.
Intro to next part
That’s all for the first part of Kylin on Cloud —— Build A Data Analysis Platform on the Cloud in Two Hours, please see part 2 here: Kylin on Cloud —— Quickly Build Cloud Data Analysis Service Platform within Two Hours (Part 2)
