Use Star Schema Benchmark for Apache Kylin
Background
For many Apache Kylin users, when deploying Kylin in the production environment, how to measure Kylin’s performance before delivering to the business is a problem. A performance benchmark can help to find the potential performance issues, so you can tune the configuration to improve the overall performance. The tunning may include Kylin’s own Job and Query, concurrent building of Cubes, HBase write and read, MapReduce or Spark parameters and more.
SSB Introduction
Kyligence Inc provides an SSB (Star Schema Benchmark) project called ssb-kylin on github, which is modified from the TPC-H benchmark, and specifically targeted to test tools in the star model OLAP scenario.
The test process generates 5 tables, and the data volume can be adjusted by parameters. The table structure of SSB is shown below:
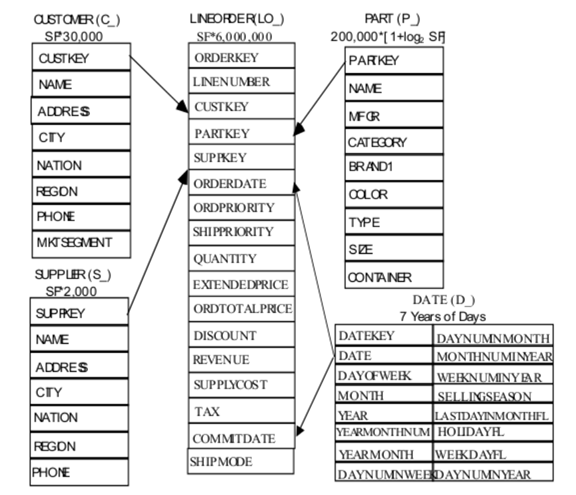
The table “lineorder” is the fact table, the other four are dimension tables. Each dimension table is associated with the fact table by the primary key, which is a standard star schema.
The environment for this test is CDH 5.13.3, which enables authentication and authorization of Kerberos and OpenLDAP, and uses Sentry to provide fine-grained, role-based authorization and multi-tenant management. However, the official “ssb-kylin” does not involve the processing of permissions and authentication, so I have slightly modified it. For details, see my fork jiangshouzhuang/ssb-kylin.
Prerequisites
** Here is a description of the Kylin deployment:**
1. Kylin deploys integrated OpenLDAP user unified authentication management
2. Add Kylin deployment user kylin_manager_user in OpenLDAP (user group is kylin_manager_group)
3. The Kylin version is apache-kylin-2.4.0
4. Kylin Cluster configuration (VM):
Kylin Job 1 node: 16GB, 8Cores
Kylin Query 2 nodes: 32GB, 8Cores
A few points before SSB pressure measurement:
1 Create a database named ssb in the Hive database.
# Log in to the hive database as a super administrator. Create database SSB; CREATE ROLE ssb_write_role; GRANT ALL ON DATABASE ssb TO ROLE ssb_write_role; GRANT ROLE ssb_write_role TO GROUP ssb_write_group; # Then add kylin_manager_user to kylin_manager_group in OpenLDAP, so kylin_manager_user has access to the ssb database.
2 Assign HDFS directory /user/kylin_manager_user read and write permissions to kylin_manager_user user.
3 Configure the HADOOP_STREAMING_JAR environment variable under the kylin_manager_user user home directory.
Export HADOOP_STREAMING_JAR=/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/hadoop-streaming.jar
Download the SSB tool and compile
You can quickly download and compile the ssb test tool by entering the following command in the linux terminal.
git clone https://github.com/jiangshouzhuang/ssb-kylin.git
cd ssb-kylin
cd ssb-benchmark
make clean
make
Adjust the SSB parameters
In the ssb-kylin project, there is a ssb.conf file below the bin directory, which defines the base data volume of the fact table and the dimension table. When we generate the amount of test data, we can specify the size of the scale so that the actual data is base * scale.
Part of the ssb.conf file is:
# customer base, default value is 30,000
customer_base = 30000
# part base, default value is 200,000
part_base = 200000
# supply base, default value is 2,000
supply_base = 2000
# date base (days), default value is 2,556
date_base = 2556
# lineorder base (purchase record), default value is 6,000,000
lineorder_base = 6000000
Of course, the above base parameters can be adjusted according to their actual needs, I use the default parameters.
In the ssb.conf file, there are some parameters as follows.
# manufacturer max. The value range is (1 .. manu_max)
manu_max = 5
# category max. The value range is (1 .. cat_max)
cat_max = 5
# brand max. The value range is (1 .. brand_max)
brand_max = 40
The explanation is as follows:
manu_max, cat_max and brand_max are used to define hierarchical scale. For example, manu_max=10, cat_max=10, and brand_max=10 refer to a total of 10 manufactures, and each manufactures has a maximum of 10 category parts, and each category has up to 10 brands. Therefore, the cardinality of manufacture is 10, the cardinality of category is 100, and the cardinality of brand is 1000.
# customer: num of cities per country, default value is 100
cust_city_max = 9
# supplier: num of cities per country, default value is 100
supp_city_max = 9
The explanation is as follows:
cust_city_max and supp_city_max are used to define the number of city for each country in customer and supplier tables. If the total number of country is 30, and cust_city_max=100, supp_city_max=10, then the customer table will have 3000 different city, and the supplier table will have 300 different city.
Prompt:
In this pressure test, the resources allocated by Yarn are used to generate test data. If the memory problems are encountered in the process of generating the data, increase the memory size of the Yarn allocation of container.
Generate test data
Before running the ssb-kylin/bin/run.sh script, explain several points to run.sh:
1 configuring HDFS_BASE_DIR as the path to table data, because I give kylin_manager_user the right to read and write to /user/kylin_manager_user directory, so configure here:
HDFS_BASE_DIR=/user/kylin_manager_user/ssb
The temporary and actual data will be generated under this directory when you run run.sh.
2 configure the LDAP user and password for deploying Kylin, and operate KeyTab files such as HDFS.
KYLIN_INSTALL_USER=kylin_manager_user
KYLIN_INSTALL_USER_PASSWD=xxxxxxxx
KYLIN_INSTALL_USER_KEYTAB=/home/${KYLIN_INSTALL_USER}/keytab/${KYLIN_INSTALL_USER}.keytab
3 configure the way that beeline accesses the hive database.
BEELINE_URL=jdbc:hive2://hiveserve2_ip:10000
HIVE_BEELINE_COMMAND="beeline -u ${BEELINE_URL} -n ${KYLIN_INSTALL_USER} -p
${KYLIN_INSTALL_USER_PASSWD} -d org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver"
If your CDH or other big data platform is not using beeline, but hive cli, please modify it yourself.
Once everything is ready, we start running the program and generate test data:
cd ssb-kylin
bin/run.sh --scale 20
We set the scale to 20, the program will run for a while, the maximum lineorder table data has more than 100 million. After the program is executed, we look at the tables in the hive database and the amount of data:
use ssb;
show tables;
select count(1) from lineorder;
select count(1) from p_lineorder;
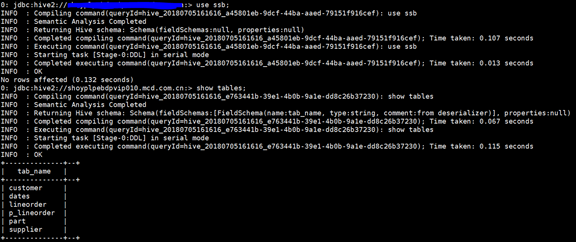
As you can see, a total of five tables and one view were created.
Load the cube’s metadata and build the cube
The ssb-kylin project has helped us build the project, model, and cube in advance. Just import the Kylin directly like the learn_kylin example. Cube Metadata’s directory is cubemeta, because our kylin integrates OpenLDAP, there is no ADMIN user, so the owner parameter in cubemeta/cube/ssb.json is set to null.
Execute the following command to import cubemeta:
cd ssb-kylin
$KYLIN_HOME/bin/metastore.sh restore cubemeta
Then log in to Kylin and execute Reload Metadata operation. This creates new project, model and cube in Kylin. Before building cube, first Disable, then Purge, delete old temporary files.
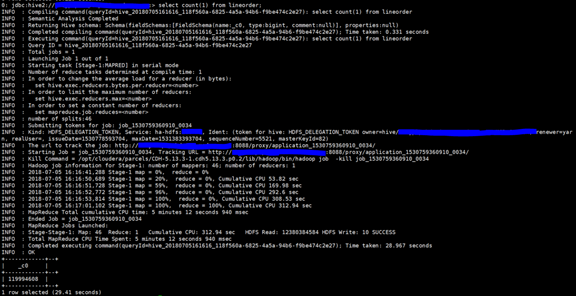
The results of building with MapReduce are as follows:
Here I test the performance of Spark to build Cube again, disable the previously created Cube, and then Purge. Since the Cube is used by Purge, the useless HBase tables and HDFS files need to be deleted. Here, manually clean up the junk files. First execute the following command:
${KYLIN_HOME}/bin/kylin.sh org.apache.kylin.tool.StorageCleanupJob --delete false
Then check whether the listed HBase table and the HDFS file are useless. After confirming the error, perform the delete operation:
${KYLIN_HOME}/bin/kylin.sh org.apache.kylin.tool.StorageCleanupJob --delete true
When using Spark to build a cube, it consumes a lot of memory. After all, using memory resources improves the speed of cube building. Here I will list some of the parameters of Spark in the kylin.properties configuration file:
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.master=yarn
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.submit.deployMode=cluster
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.yarn.queue=root.kylin_manager_group
# config Dynamic resource allocation
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled=true
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.minExecutors=10
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors=1024
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.dynamicAllocation.executorIdleTimeout=300
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.shuffle.service.enabled=true
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.shuffle.service.port=7337
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.driver.memory=4G
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.executor.memory=4G
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.executor.cores=1
kylin.engine.spark-conf.spark.network.timeout=600
The above parameters can meet most of the requirements, so users basically do not need to configure when designing the Cube. Of course, if the situation is special, you can still set Spark-related tuning parameters at the Cube level.
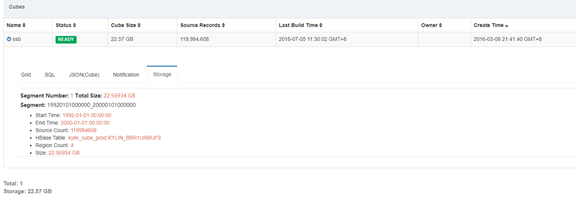
Before executing Spark to build a Cube, you need to set the Cube Engine value to Spark in Advanced Setting and then execute Build. After the construction is completed, the results are as follows:
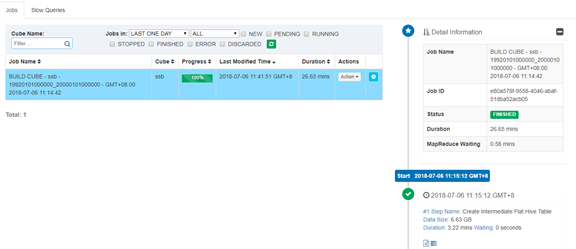
In contrast, the time for MapReduce and Spark to build Cube is as follows: (Scale=20):
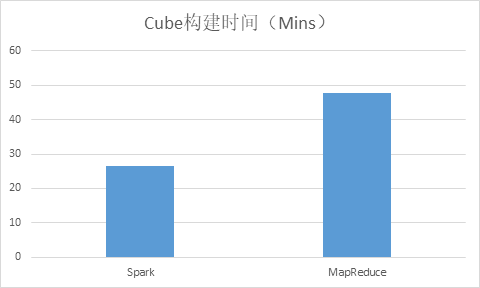
You can see that the speed of building is almost 1x faster. In fact, Spark has many other aspects of tuning (performance can be improved by 1-4 times and above), which is not involved here.
Query
Ssb-kylin provides 13 SSB query SQL lists. The query conditions may vary with the scale factor. You can modify the results according to the actual situation. The following examples show the test results in the case of scale 10 and 20:
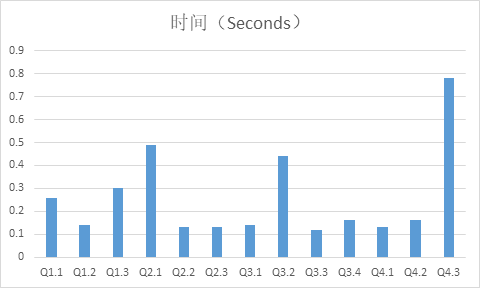
The query result of Scale=10 is as follows:
The query result of Scale=20 is as follows:
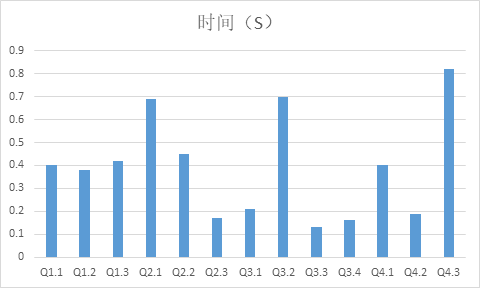
As can be seen from the results, all the queries are completed within 1 s, which proves Apache Kylin’s subsecond query capability strongly. In addition, the average performance of the query did not decrease significantly as the amount of data doubled, which is also determined by the theory of Cube precomputation.
Note: For details on each query statement, see the README.md description in the ssb-kylin project.
At this point, the Kylin’s SSB pressure test is completed, but for you who are reading the article, everything is just beginning.
