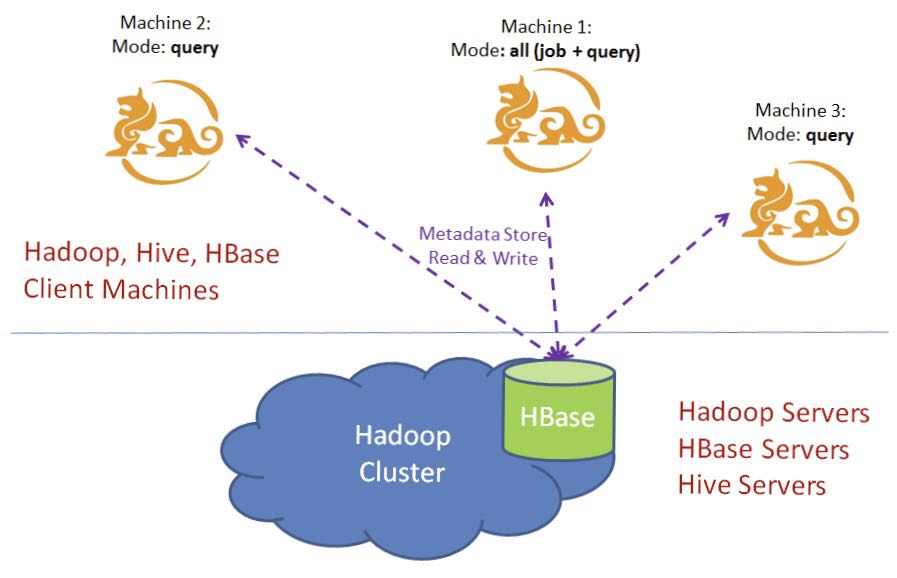
Kylin Server modes
Kylin instances are stateless, the runtime state is saved in its metadata store in HBase (specified by kylin.metadata.url in conf/kylin.properties). For load balance considerations it is recommended to run multiple Kylin instances sharing the same metadata store, thus they share the same state on table schemas, job status, Cube status, etc.
Each of the Kylin instance has a “kylin.server.mode” entry in conf/kylin.properties specifying the runtime mode, it has three options:
- job : run job engine in this instance; Kylin job engine manages the jobs to cluster;
- query : run query engine only; Kylin query engine accepts and answers your SQL queries;
- all : run both job engine and query engines in this instance.
Notice that only one instance can run the job engine (“all” or “job” mode), the others must be “query” mode.
A typical scenario is depicted in the following chart:
Configure Multiple Kylin Servers
If you are running Kylin in a cluster where you have multiple Kylin server instances, please make sure you have the following property correctly configured in conf/kylin.properties for EVERY instance.
kylin.rest.servers
List of servers in use, this enables one instance to notify other servers when there is event change. For example:
kylin.rest.servers=host1:7070,host2:7070
kylin.server.mode
Make sure there is only one instance whosekylin.server.modeis set to “all” or “job”, others should be “query”
kylin.server.mode=all
Setup Load Balancer
To enable Kylin service high availability, you need setup a load balancer in front of these servers, letting it routes the incoming requests to the cluster. Client side communicates with the load balancer, instead of with a specific Kylin instance. The setup of load balancer is out of the scope; you may select an implementation like Nginx, F5 or cloud LB service.
